Crypto OTC Trading Platform
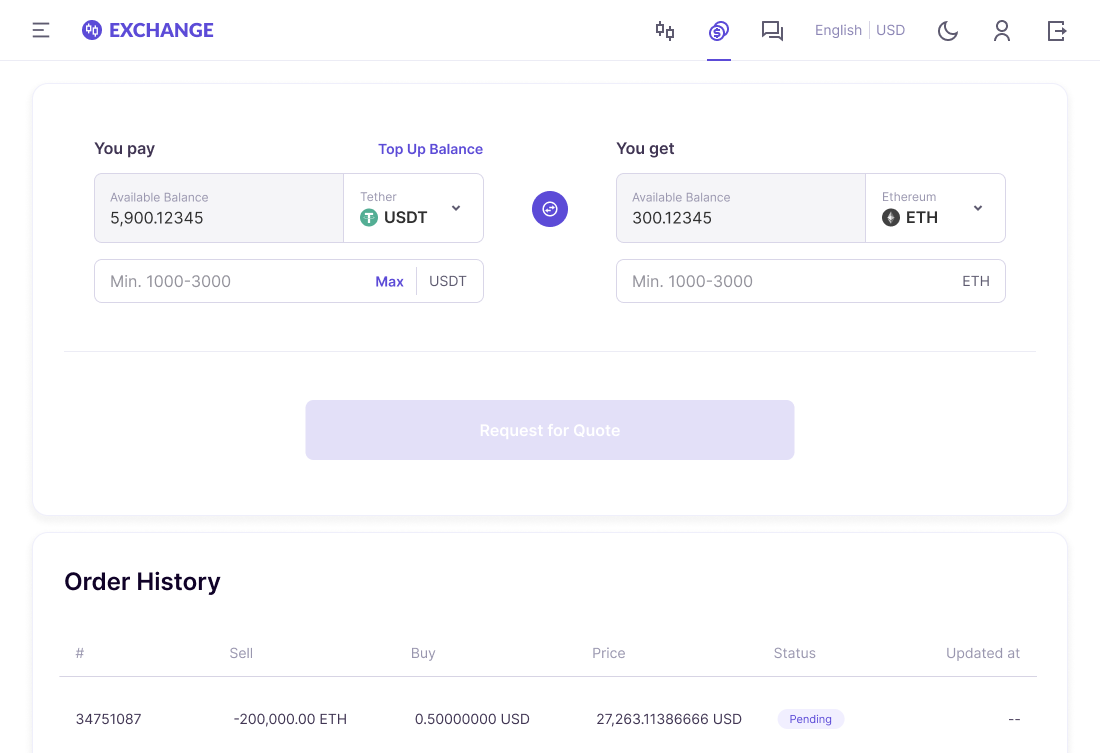
Merkeleon crypto OTC trading technology with a request for quotes process (RFQ) allows executing instant operations in large amounts. The product is suitable for institutional customers and businesses that execute OTC transactions daily. Business accounts can transact virtual assets there. The product is a one-stop shop. It has a complete functionality to be launched on a client’s site within 3 weeks.


Merkeleon has built an OTC crypto exchange solution to help enterprises launch an over-the-counter site for virtual assets. This technology has an RFQ module that guarantees a special exchange rate of transacted crypto within specified time. The technology supports popular virtual and fiat currencies: BTC, ETH, USDT; USD, EUR, AED. Providers can connect this technology to other services via API.
Exchanges Launched Worldwide
Audited Cryptocurrency Exchange Solution
Years of Crypto Exchange Development
Years of Software Development
Features of OTC Crypto Trading Software
-
Convenient API for enterprises
-
Most demanded cryptocurrencies
-
Adjustable system for any trade traffic
-
Large pool of liquidity with leverage
-
Automated KYB verification
-
Advanced Financial Reporting Tools
Platform Functional Characteristics
The intuitive solution for an OTC crypto trading platform ensures the user-friendly management of traditional and virtual currencies. This technology is equipped with adaptable operational processes and features an easy-to-use interface.
Exchange or OTC Trading for Bitcoin and Other Currencies
OTC software enables a website for transacting extensive sums of cryptocurrency, hundreds of thousands of USD. The software, nevertheless, can be set at a lower minimal transacted amount, dozens of thousands of USD.
With this technology, providers guarantee business clients, investors, banks, brokers, secure operations. Clients go to OTC environments when they need to transact serious money, stocks.
Centralized exchanges maintain great transactions too. There are a few complications, however. First, a website may lack the requested sum due to the lack of liquidity, insufficient reserves. Further, once an order is in process, it boosts the value of a transacted virtual currency.
Since the demand for this asset grows, its value grows accordingly and causes strong fluctuations in the currency rate, just like stocks work. In 2013, a client bought 25,000 of bitcoin worth 15 million USD. The currency value climbed from initial 600 USD to 700 USD.
Market rates during over-the-counter trading are higher. Yet, it ensures the price stability impossible on an exchange. After all, even such a markup makes OTC operations profitable for major transactions with virtual assets.



 Contact form
Contact form
Contact Us
OTC Trading Crypto Maintained
To launch an over-the-counter website for transactions with virtual money, software is not enough. Providers need a full-fledged support, from financial advisors to legal and marketing specialists. Merkeleon in collaboration with partners offer services that set a business into action quickly and painlessly.
Business assistance
Our partners help you open a business account with an IBAN that allows international transactions. You will have information about preferable jurisdictions for blockchain companies, the price of account service, time for opening an account. Also, you will know about the option of remote opening a bank account. The partners will assist with application forms and technical support.
Legal assistance
You get information about favorable jurisdictions and legal frameworks for setting up a blockchain enterprise. Within legal assistance, you will register a company in a chosen jurisdiction. Merkeleon and partners help settle documents, prepare the company’s rules of order and KYC rules. You will also have documents translated into the required language.
Marketing assistance
Your platform will enter the market and become a well-known site to trade big amounts of bitcoin and other currencies. For promotion, we use various means: affiliate systems, blockchain consulting, newsletters, reputation management, influencer marketing, social media. Our specialists help with content marketing: SEO-promotion, whitepaper writing, press releases, blogs.
FAQ
What is an OTC broker?
It is a destination for large transactions. Such platforms allow approved business customers to buy, sell, lend, borrow, swap big amounts of virtual currencies without affecting market rates. To learn how platforms with OTC trading work, read this article.
What is the best OTC broker?
This platform features security, confidentiality, liquidity. Security is achieved with cold storage, insurance policy, reputation. Confidentiality builds on the reliability of a broker and counterparties to a transaction. Liquidity comes from connected liquidity providers and the volume of trading. The most popular websites on the market are Binance, Coinbase Prime, Kraken, Coinsquare Wealth, CoinSmart Premium, Satstreet.
What is the difference between OTC crypto trading and exchange?
The main difference between over-the-counter crypto exchange and traditional crypto exchanges is unique terms. On exchanges, prices are determined by supply and demand, whereas OTC desks allow its participants to negotiate any volume and price, sometimes with a significant discount or surcharge to the stock price.
Furthermore, exchange traders have to make many small transactions to trade a big sum, which, in turn, triggers rates. At that time, it is liquidity, volatility, and spread that determine the number of required transfers. Therefrom, price fluctuations ultimately upscale trading rates and cripple participants.
That said, in OTC trading, clients have one large transaction that can nonetheless be divided into smaller portions. The stipulated initial price, however, remains, which helps traders to increase efficiency and escape price slippage.
How to launch an OTC crypto desk?
You need special software, turnkey or built from scratch. An OTC site can be based on an existing cryptocurrency exchange, as an additional functionality to a trader’s toolkit. Besides, it can be part of an ecosystem that provides clients various services: NFT marketplace, auctions, crypto games. Alternatively, you can make it a separate platform meant exclusively for ample investors and financial institutions.
How to automate an OTC platform?
After customizing software, approved business customers conclude deals automatically. They place an order, specifying time limits and minimum sum payable. If a customer has enough money deposited in the wallet, the algorithm will execute a transaction when all the requirements are met.
How does cryptocurrency OTC trading work?
OTC settlements are a complex procedure comprised of verification, negotiation, and transfer stages. Let’s discover what peculiarities it has.
Step 1: Know Your Client
An outstanding OTC platform is not merely a medium, as with p2p domains, where users purchase small doles of cryptocurrency from each other. A licensed provider is liable to its customers and conducts KYC checks to verify counterparties for compliance with the rules of anti-laundering legislation.
Step 2: Negotiate Price
An over-the-counter procedure itself begins with an online request and a further search for a counterparty. When such a partner is found, they inform about their preferred volume and price, which may be 1-5% higher than the market rate. Then, it the seller’s turn whether they agree, cancel or negotiate this deal.
Step 3: Money Transfer
When both parties reach an agreement as to the size and price of this arrangement, they can exchange their assets. Usually, they send money directly to electronic wallets. Another option is to make a bank transfer.
What are the types of crypto OTC desks?
Cryptocurrency over-the-counter desks are divided into Principal and Agency ones that differ in the risking party. With Principal desks, it is an OTC platform that carries risks trading with its own money on behalf of a client. Agency OTC services, on the contrary, act as an intermediary that buys assets for client’s money.
In both scenarios, there is a probability that services may fail to find a counterparty before asset prices jump. Principal OTC desks lose profit in this case as their goal is to secure a cost lower than the market, whilst Agency OTC traders stop searching until a client updates their agreement.
Why trade crypto via OTC trading platform?
A general challenge with almost any cryptocurrency asset is that it has insufficient liquidity. Besides. almost any massive transaction can greatly impact exchange rates. Over-the-counter combats this setback and guarantees a few other advantages:
- Greater transactions. OTC platforms enable enough liquidity to work with large amounts;
- Saved money. Most services do not charge commissions;
- Maintained confidentiality. Some OTC domains provide anonymous transactions, without entering data into registers;
- Price stability. The negotiated price has no impact over currency rates and stays the same until a deal ends;
- Functional independence. OTC platforms operate at weekends and in periods of high volatility.
In the crypto sphere, the OTC market has long been the environment for the whales, whose deals start at $50,000-100,000. Now, anyone can benefit in OTC deals with just $3,000 by purchasing a part of a huge lot with a lucrative discount, due to emerging DeFi OTC desks.
What risks does crypto OTC trading have?
OTC domains managing big money are an attractive tool for giant investors. We are witnessing the formation and growth of a private cryptocurrency banking, which will become an alternative for clients who want to diversify their investments. Yet, there are a few drawbacks to consider:
- High risk. White destinations neutralise the chance of fraudsters joining over-the-counter trading through thorough KYC and AML. Meanwhile, the members of the grey segment stay at risk;
- Few currencies. OTC sites run with a modest range of crypto, which, nevertheless, incorporates major ones, bitcoin, ether, litecoin;
- Information leakage. Even though OTC deals do not affect price directly, insider information can be revealed and spur fluctuations.
Any trade entails risks. In over-the-counter, it is particularly crucial to scan counterparties to eliminate any probability for a client to unintentionally engage in questionable or criminal activities. You can reduce risks if you choose a trusted over-the-counter desk.
How does secure crypto desk look like?
A chief criterion for finding a proper OTC providers is their ability to transact in fast-growing markets under high volatility and illiquidity. The best services adapt to market uncertainty, balancing between confidence and humility, and offer their customers facility and liquidity. Other parameters embody:
- Cold storage;
- Reserve fund;
- Solid reputation.
Moreover, no need to mention a license. In spite of unlicensed desks being more profitable, the risks they encapture, from money theft to copartnership, go beyond potential revenue. White agencies are regulated, meaning clients are protected by the legislation of a certain jurisdiction.